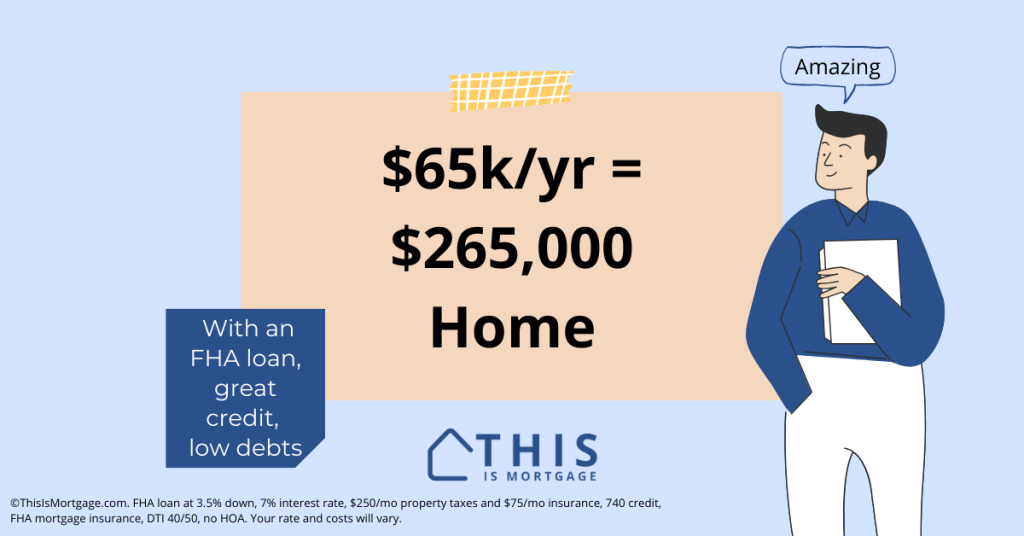
If I Make $65,000 A Year What Mortgage Can I Afford?
You can afford a home up to $265,000 with a mortgage of $260,200.
This assumes a 3.5% down FHA loan at 7%, a base loan amount of $255,725 plus the FHA upfront mortgage insurance premium of 1.75%, low debts, good credit, and a total debt-to-income ratio of 50%.
Keep in mind that there are many factors that affect this number including property taxes, homeowner’s insurance, HOA dues, and more. Apply with a lender to find your personalized maximum home price.
Speak to our lending team to see what you can afford with a $65k salary.
$65k income mortgage payment breakdown
There’s more to your housing payment than just principal and interest. Lenders consider property taxes, homeowners insurance, and HOA dues as part of your payment when qualifying you.
| Part of payment | Amount |
| Principal & interest | $1,731 |
| Monthly mortgage insurance | $119 |
| Taxes | $250 |
| Homeowner’s insurance | $75 |
| HOA dues | $0 |
| Total payment based on these assumptions (40% DTI) | $2,175 |
See assumptions for all calculations at the bottom of this article.
Home affordability by monthly debt payments
Your debt level affects your buying power perhaps more than anything else.
For instance, say you have $500 in monthly debt such as student loans and credit card payments. This amount of debt isn’t hurting you much at a salary of $65,000 per year. But adding an additional $500-per-month auto payment would reduce your maximum home price to just $200,000 instead of $265,000.
Lenders can approve you to use up to about half your gross monthly income toward debt payments. That’s $2,708 for an annual salary of $65,000. About 40% of your gross income ($2,167) can be used for the house payment leaving about 10% for other debts.
| Yearly income | $65,000 |
| Monthly income | $5,417 |
| Max house payment (40%) | $2,167 |
| Max total debt payments (50%) | $2,708 |
In mortgage-speak, that’s a 40% front-end debt-to-income (DTI) ratio and a 50% back-end DTI. Borrowers with good credit can be approved with higher ratios, but to be safe we are using these numbers.
Following is what you might qualify for depending on your current debt load.
| Annual Income | Monthly Debt | Max House Payment | Max Home Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| $65,000 | $0-$540 | $2,167 | $265,000 |
| $65,000 | $750 | $1,950 | $240,000 |
| $65,000 | $1,000 | $1,700 | $200,000 |
| $65,000 | $1,250 | $1,450 | $165,000 |
| $65,000 | $1,500 | $1,200 | $125,000 |
Related: Buying a Home With Zero Down Payment
Connect with a lender to see what you can afford.
Maximum home price by down payment
Your down payment dramatically affects affordability.
For one, your loan balance drops with a higher down payment, resulting in a lower payment. Additionally, you pay less mortgage insurance when you put more down.
| Annual Income | Down Payment | Monthly Payment | Home Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| $65,000 | 3.5% | $2,167 | $265,000 |
| $65,000 | 5% | $2,167 | $270,000 |
| $65,000 | 10% | $2,167 | $290,000 |
| $65,000 | 20% | $2,167 | $340,000 |
No down payment? Speak to a lender now about down payment assistance programs.
Maximum home price by interest rate
Interest rate is another significant determiner of your maximum home price. If rates drop, it’s a great time to enter your home search.
| Annual Income | Interest Rate | Monthly Payment | Home Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| $65,000 | 8% | $2,167 | $245,000 |
| $65,000 | 7% | $2,167 | $265,000 |
| $65,000 | 6% | $2,167 | $295,000 |
| $65,000 | 5% | $2,167 | $325,000 |
Maximum home price by desired debt-to-income level
While many financial gurus suggest you have a debt-to-income of 25% or less, it’s unrealistic in most markets. Pushing your front-end (housing) DTI from 25% to 40% increases your buying power by over $100,000 at an income of $65,000.
| Annual Income | DTI | Max Payment | Home Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| $65,000 | 25% | $1,250 | $150,000 |
| $65,000 | 40% | $2,167 | $265,000 |
Ways to increase your buying power
If you’re struggling to find a home that you can qualify for, there are ways to increase your maximum loan amount and purchase price.
Consider an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM): As seen above, reducing your rate from 7% to 6% can increase your buying power by $30,000 at your income level. An ARM rate eventually adjusts but starts off fixed for at least 3-5 years. That’s a lot of time to refinance or increase your income to afford a potentially higher payment later.
Avoid HOAs. Homeowner association dues can be hundreds of dollars per month. Dues add to your DTI which limits your buying power.
Make a bigger down payment or get gift funds. The lower your mortgage balance, the lower your payment will be. Try to find a down payment assistance program or get a gift from family to reduce your loan amount.
Use an FHA loan. These tend to be most lenient on debt-to-income ratios. Conventional loans limit you to about 45% DTI including all debts and housing payment (50% in select cases). FHA’s max is 46.9% front-end DTI and 56.9% back-end for well-qualified buyers.
Pay off debt: Paying off a $500 car payment can increase your buying power by $75,000.
Request a call from a lender to see what you can afford with a $65k salary.
FAQ
You may be able to afford a $265,000 home with an FHA loan of $260,200. Your exact amount depends on your debts, interest rate, property taxes, homeowner’s insurance, HOA dues, loan program, and payment comfort level.
Reducing your debt payments by $500 per month can increase your maximum home price by about $70,000 if you make $65,000 per year. Paying off debt will help you qualify for a better home that will suit your needs longer.
You don’t need a high credit score. An FHA loan requires just a 580 score and allows for high debt-to-income ratios. However, a higher credit score will help you qualify for a larger loan.
$65,000 income isn’t too low to buy a house.
You may have been told that you can’t afford a home on $65,000 per year. But if you’re creative and committed to becoming a homeowner, you can very likely make it happen.
Speak to a lending professional to see if you are eligible to buy a home.
All calculations assume a 3.5% down FHA loan at 7%, $250/mo property taxes and $75/mo insurance, FHA mortgage insurance, conventional mortgage insurance for 5% & 10% down scenarios, 740 credit score, no HOA, $500 or less in monthly debt payments. Your rate and costs will vary.